🖥️ Understanding WebLogic Heap Memory: Components, Usage & Garbage Collection 🔄
Efficient memory management is crucial for Oracle WebLogic Server, ensuring applications run smoothly without performance bottlenecks. In this blog, we’ll break down heap memory components, how they’re utilized, and how Garbage Collection (GC) works in WebLogic, including Full GC vs Partial GC (Minor GC). 🚀
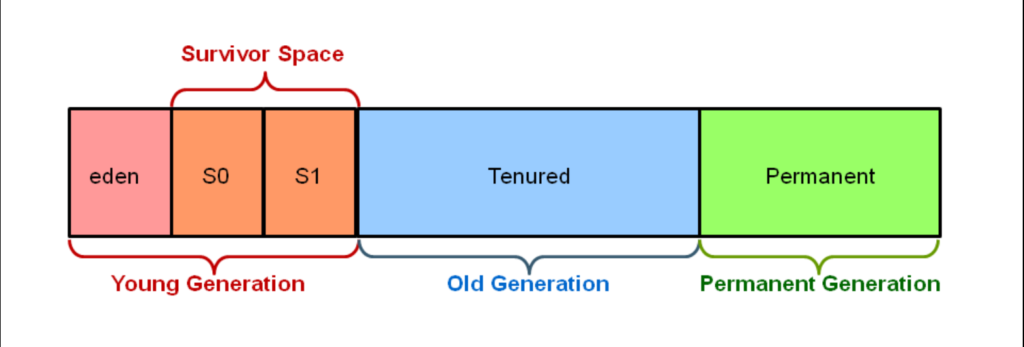
🔍 What is Heap Memory in WebLogic?
Heap memory is the runtime memory allocated to a Java application. In WebLogic, the JVM heap is divided into several components to manage objects efficiently. It plays a crucial role in application performance, ensuring smooth execution by dynamically managing memory allocation and deallocation.
🛠️ Key JVM Heap Parameters:
-Xms👉 Defines the initial heap size, which is allocated when the JVM starts.-Xmx👉 Defines the maximum heap size, ensuring the application does not exceed memory limits.-XX:NewRatio👉 Adjusts the ratio of young to old generation, helping optimize object allocation.
📌 Components of Heap Memory
1️⃣ Young Generation (Eden + Survivor Spaces) 🌱
The Young Generation stores newly created objects, and it is designed for short-lived objects. It consists of:
- Eden Space 🛠️: Where all new objects are initially allocated. A high percentage of objects in Eden never make it to the next stage.
- Survivor Spaces (S0 & S1) 🔄: Objects that survive Minor GC move here before being promoted to the Old Generation.
🔹 How it Works: ✅ When the Eden space fills up, Minor GC (Half GC) is triggered. ✅ Objects that survive multiple GC cycles in Survivor Spaces are promoted to the Old Generation. ✅ Minor GC is fast and frequent, keeping Young Gen clean.
2️⃣ Old Generation (Tenured Space) 🏗️
Long-lived objects that survive multiple Young Generation GC cycles move to the Old Generation. This space contains large, persistent objects that remain for extended periods.
🔹 How it Works: ✅ Full GC is used to clean up the Old Generation when memory becomes full. ✅ Objects that live long enough in the Young Generation graduate to this space. ✅ If this space gets too full, application performance drops due to frequent Full GC events.
3️⃣ Metaspace (Java 8+ Replaces PermGen) 🏛️
Unlike the old PermGen (Permanent Generation), which had a fixed size, Metaspace grows dynamically based on class metadata.
🔹 Key Features: ✅ Stores class metadata, JIT optimizations, and reflection data. ✅ Dynamically expands and is not subject to -Xmx heap limits. ✅ Configured with -XX:MetaspaceSize and -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize.
🔄 Garbage Collection in WebLogic
WebLogic relies on Garbage Collection (GC) to manage memory efficiently. There are two main types of GC:
⚡ 1. Minor GC (Half GC) 🔄
✅ Only affects Young Generation (Eden + Survivor Spaces). ✅ Happens frequently but is fast. ✅ Causes minimal application pause time. ✅ Uses Copying GC algorithm to move objects efficiently between Young Gen spaces.
🔹 When Does Minor GC Occur?
- When Eden space is full.
- JVM reclaims memory from short-lived objects.
- Helps keep overall memory usage low and prevents premature promotion to Old Generation.
🚨 2. Major/Full GC 🛑
✅ Cleans up both Young and Old Generation. ✅ Stops the entire application (Stop-the-World Event), causing longer pauses. ✅ Uses Mark-Sweep-Compact algorithm to clean memory.
🔹 When Does Full GC Occur?
- Heap usage is high, and objects can’t be promoted.
- Explicit calls to System.gc() (not recommended).
- Old Generation fills up, triggering a Stop-the-World GC event.
- Metaspace memory pressure forces additional cleanup cycles.
🏗️ Optimizing Heap Memory & GC Performance
To reduce Full GC pauses and optimize memory: ✅ Tune Heap Size: Adjust -Xms and -Xmx values based on application needs to avoid memory fragmentation. ✅ Use G1 GC or ZGC for low-latency applications, reducing pause times. ✅ Monitor GC Logs: Enable GC logging with:
-XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCDateStamps -Xloggc:/path/to/gc.log✅ Adjust Survivor Ratios: Use -XX:SurvivorRatio=8 to fine-tune Young Gen for better GC efficiency. ✅ Avoid System.gc(): It triggers Full GC, leading to unnecessary application pauses.
📌 Conclusion
Heap memory management in WebLogic plays a critical role in application stability and performance. Understanding Young & Old Generations, optimizing Garbage Collection, and tuning JVM parameters can help you achieve optimal performance. 🚀
✅ Monitor memory usage regularly using JVisualVM or Java Mission Control. ✅ Optimize JVM parameters based on application workload. ✅ Prevent unnecessary Full GC events by tuning Old Gen allocations correctly.
🤝 Connect With Us
Are you looking for certified WebLogic professionals or need expert guidance on your project? We are here to help!
- 🔹 Get Certified Candidates: Hire skilled professionals with WebLogic expertise.
- 🔹 Project Consultation: Get best practices and hands-on support for seamless implementation.
📞 Contact Us Now
💼 Discuss Your Project
💬 How do you manage GC in WebLogic? Share your insights below! 😊
#WebLogic #Java #JVM #GarbageCollection #PerformanceTuning #CloudComputing
